丁香通授权总的代理认证如上:
无水货途径,拒绝假冒伪劣产品,维护客户权益和品牌形象!
Fluorochrome 公司郑重声明:荧光金(Fluoro-Gold)是Fluorochrome 公司经过多年研究开发出来的 专利产品,真正Fluoro-Gold(Fluorogold)仅由Fluorochrome公司以及 各地区授权代理销售。Fluoro-Gold自1985年以来被广泛使用,有大量科研文献。其他公司营销产品时声称他们的是一样的替代或假冒Fluoro-Gold。事实上,这些化合物的化学结构与Fluoro-Gold不同,化合物的某些物理性质是非常不同的。
Fluorochrome 技术答复Fluoro-Gold与其他染料的区别如下
假冒伪劣产品特点:供应公司声称自己为品牌的一级授权代理,但均无授权证明;只宣传宣传推广品牌,没有详细产品信息,并在其他正规网站均无授权认证信息。例如单做品牌的百度推广,代理信息无法证明的;替代产品所用普通的荧光染料价格非常低廉,以假乱真有丰富的利润可图,包装简陋,均低于市场均价,效果存在明显差异,导致老师实验受到影响而重新订购。 客户和经销商朋友订购时完全可要求提供Fluorochrome公司出货单 及 可查询的国际快递单号。务必确认产品为正规来源,不要轻易相信水货假货商家。
近期收到一些水货及假货的投诉,有的导致老师实验受到严重影响,我们和Fluorochrome公司特此声明:
深圳市豪地华拓生物科技有限公司为 Fluorochrome公司在中国大陆及港澳地区的授权代理。我们可以提供完善的技术支持和售后保障。 我公司2005年开始代理和推广 Fluorochrome公司产品,其中文名称“荧光金”源自广州华拓公司,其货号“FC10001、FC20001…“为华拓公司自编货号:我们的价格优势-Fluorochrome正品国内最 。
华拓生物公司联系方式: e-mail:order@otwobiotech.com Telephone:(86)0755-26055215
Fluorochrome公司直接联系方式:e-mail: info@Fluorochorome.com Telephone:(303) 394-1000 Fax: (303) 321-1119
客户如订购到伪劣产品请保留好订购合同,收货单或快递单号等,并及时和我们联系。
Fluoro-Gold Protocol and Use Guide 荧光金使用流程指引
1. Background
The use of Fluoro-Gold is essentially the same as other fluorescent tracers. The main difference is that Fluoro-Gold is more flexible in terms of post-injection survival times, concentration range, tissue treatment and compatibility with other histochemical techniques.
2. Storage and Shelf Life
Dry Fluoro-Gold should be kept in a light tight closed container at 4 degrees Celsius. Stored properly, Fluorogold should have a shelf life exceeding one year. The dye in solution should also be kept in a light tight closed container at 4 degrees Celsius and should remain stable for at least six months.
3. Vehicle
Fluoro-Gold can be dissolved in distilled water or 0.9% saline, or utilized as a suspension in 0.2M neutralphosphate buffer.
4. Dye Concentration
Fluoro-Gold has been successfully used at concentrations ranging from 1-10%. Initially, a 4% concentration is advised. If undesirable necrosis occurs at the injection site, or labeling is too intense, reduce the concentration to a 2% solution. If you need to use more precise measurements, the molecular weight of Fluoro-Gold is 532.6 daltons.
5. Dye Administration
A. Pressure Injection - This is probably the most frequently used mode of application. Volumes injected range from .05-1μl, typically .1-.2μl.
B. Iontophoresis - Discrete, small injection sites result from 4-10 second pulsed iontophoretic (+5 to
+10ua/10min) application.
C. Crystal - A crystal of the tracer can be administered from the tip of a micro-pipette.
6. Post-Operative Survival Period
Good retrograde labeling has been observed with periods ranging from two days to two months. Survival periods of three to five days are typical. Long survival periods enhance filling of distal processes without diffusion of the dye from the cell.
7. Fixation
Almost any fixative, or no fixative, can be used, Phosphate neutral buffered saline containing 4% formaldehyde is frequently employed. Fixatives containing high concentrations of heavy metals (e.g. osmium, mercury) will quench the fluorescence, while high concentrations (over 1%) of glutaraldehyde may increase background fluorescence
8. Histochemical Processing
Tissue containing Fluoro-Gold may be processed according to virtually any common histological technique. This includes cryostat sections of unfixed tissue (10 μm), frozen sections of fixed tissue (20 μm), and thin sections cut from tissue imbedded in either plastic (.2-4 μm) or paraffin (3-10 μm). Frozen sections of fixed tissue are most frequently used.
9. Combined Methods
At this point of processing, sections may be further processed for a second marker such as autoradiography, HRP histochemistry, immunocytochemistry, a second fluorescent tracer, fluorescent counterstain, etc.
10. Mounting, Clearing and Coverslipping
Sections are typically mounted on gelatin-coated slides, air-dried, immersed in xylene, and coverslipped with nonfluorescent DPX plastic mounting media. Sections may be dehydrated with graded alcohols, unless this is not compatible with a second tracer. If Fluoro-Gold is to be combined with fluorescence immunocytochemistry, then sections are air-dried and directly coverslipped with neutral buffered glycerine (1:2).
11. Examination and Photography
Fluoro-Gold can be visualized with a fluorescence microscope using a wide band ultraviolet excitation filter. A gold color is emitted when tissue has been processed with neutral pH buffer, whereas a blue color is emitted when tissue is processed with acidic (e.g. pH 3.3) pH buffer. It can be photographed digitally or with film (use Ektachrome 200-400 ASA film for color prints and comparable speed film for black and white prints, for example Tri-X). Most exposure times range from 10-60 second exposures, depending on the objective magnification and the intensity of the label. Thirty (30) second exposures are about average. Multiple exposures may be exploited to simultaneously visualize Fluoro-Gold and another tracer. Thus, UV would be combined with bright field illumination to simultaneously locate Fluoro-Gold with HRP or silver grains in autoradiography. Similarly, blue light excitation can be combined to also visualize the green emission color of FITC, while green excitation light may be used to simultaneously observe the red emission color of propidium iodide, or ethidium bromide (a fluorescent counterstain).
Additional Information Concerning the Use of Fluoro-Gold
Vehicle
For pressure injections through a microsyringe or micropipette, Fluoro-Gold should be dissolved in distilled water or .9% saline. Fluoro-Gold may also be utilized as a suspension in .2M neutral phosphate buffer, however, the suspended particles may clog a fine micropipette tip so distilled water or .9% saline is the preferred vehicle. For iontophoresis, a 1% Fluoro-Gold solution is made up in .1M acetate buffer (pH=3.3). Well-cleaned (95% ETOH, water) glass micropipettes should have tips of 10-20 μm. Optimal iontophoresis parameters are +1 to +5u amps delivered with pulsed current (4-10 seconds on, 4-10 seconds off) over a 10-20 minute period.
Injection Sites
Virtually any central or peripheral nervous system structure can be injected with Fluoro-Gold for analysis of retrograde transport. In the peripheral nervous system, ganglia and peripheral targets can be studied. For studies of peripheral nerve, the nerve should be cut or damaged and either dipped in, or injected with, aq 5% solution of Fluoro-Gold. Since Fluoro-Gold is not significantly taken up by intact fibers of passage, the fibers must be cut or severely damaged for uptake of the dye to occur.
Transport and Survival Time
Fluoro-Gold is used as a retrograde axonal tracer, although orthograde axonal transport does occur. The survival time should be varied (especially to very short survival times of 12 hours - 2 days) to maximize orthograde transport in the specific neuronal system under study. For retrograde transport, the survival times should be varied from 4 days to 14 days. Seven to 10 days works for most systems, although long pathways (e.g., spinal cord to brainstem) and pathways in large mammals (e.g., cats, monkeys) may require longer survival times (e.g., 14 days). In addition, since Fluoro-Gold remains fast within retrogradely labeled neurons, survival times of several months will also produce excellent results. For iontophoresis, a 2-5 day survival time is recommended. It is estimated that transport occurs at about 2 cm per day for mammals; it is slower for cold-blooded animals.
Tissue Processing
Tissue processing is covered in detail in the use guide and in the original publication (Schmued and Fallon, 1986, Brain Research 377:147-154). Since Fluoro-Gold is stable in many solvents and remains fast within retrogradely labeled neurons, it's use is compatible with many histochemical techniques. It can be used with other retrograde tracers, immunofluorescence, PAP and ABC immunocytochemistry, HRP histochemistry, autoradiography, counterstains (ethidium bromide is the preferred fluorescent counterstain), paraffin embedding and plastic embedding. However, if tissue is unfixed, additional processing of tissue in aqueous solutions for over an hour or two will result in loss of Fluoro-Gold fluorescence from labeled neurons. Fluoro-Gold may be useful in electron microscopy. Fluoro-Gold can be used in a brain which has been sectioned and transferred to phosphate buffer. Sections are typically mounted on gelatin-coated slides, air dried, immersed in xylene and coverslipped with DPX plastic mounting media (FLUKA Chemical Corp., 255 Oser Avenue, Hauppauge, New York, 11788, Catalog #44581). Tissue may also be viewed on slides without further processing, can be run through graded alcohols for dehydration, or, for immunocytochemistry, the sections can be air dried and directly coverslipped with neutral buffered glycerine (1:2).
Examination and Photography
Fluoro-Gold is visualized with a fluorescence microscope using a wide band ultraviolet (UV) excitation filter. Use the same filter pack you would for other fluorescent retrograde tracers excited under wide band UV (e.g., True Blue, Fast Blue, Nuclear Yellow), such as the Leitz Ploem filter system A (Wide Band UV, Excitation filter BP 340-380), Mirror RKP 400, Barrier Filter LP 430). Objectives should be made especially for fluorescence microscopy (such as that made by Zeiss) glycerine, or water. Since plastic does absorb UV light, it is not advised to view through plastic petri dishes, etc. Recommended films are T-Max (Kodak, black & white) and Ektachrome 200 (Kodak, color slides). Exposure times usually vary from 20 seconds to 1.5 minutes.
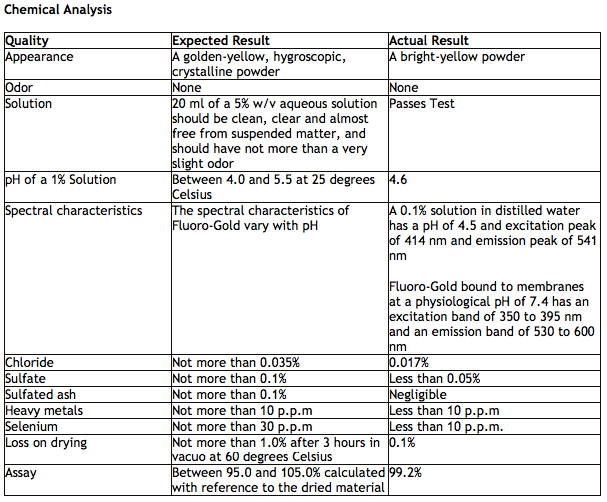
.jpg)
部分荧光金Fluoro gold文献:
Tosolini A.P., Mohan R, Morris R., “Targeting the full length of the motor end plates regions in the mouse forelimb increases the uptake of Fluoro-Gold into corresponding spinal cord motor neurons,” Frontiers in Neurology (2013) 1-10.
Tosolini A.P., Mohan R., “Spatial characterization of the motor neuron columns supplying the rat forelimb,” Neuroscience 200 (2012) 19-30.
Bowyer, J.F. and Schmued, L., Fluoro-Ruby labeling prior to an amphetamine neurotoxic insult shows a definitive massive loss of dopaminergic terminals and axons in caudateputamen. Brain Res., 1075, (2006) 236-239.
*Schmued, L.C., “Anti-retrograde and retrograde neuroanatomical tract tracing with fluorescent compounds,” Neuroscience Protocols, 94-050-02 (1994) 1-15.
Van Bockstaele, E.J., Wright, A.M., Cestari, D.M., and Pickel, V.M., “Immunolabeling of retrogradely transported Fluoro-Gold: sensitivity and application to ultrastructural analysis of transmitter-specific mesolimbic circuitry,” Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 55 (1994) 65-78.
*Bowyer, J.F., Gough, B., Broening, H.W., Newport, G.D., and Schmued, L., “Fluoro-Gold and Pentamidine Inhibit the In Vitro and In Vivo Release of Dopamine in the Striatum of Rat,” The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 266 (1993) 1066-1074.
Balercia, G., Chen, S., and Bentivoglio, M., “Electron microscopic analysis of fluorescent neuronal labeling after photoconversion,” Journal of Neuroscience Methods 45 (1992) 87-98. [Link]
*Chang, H.T., Kuo, H., Whittaker, J.A., and Cooper, N.G.F., “Light and electron microscopic analysis of projection neurons retrogradely labeled with Fluoro-Gold notes on the application of antibodies of Fluoro-Gold,” Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 35 (1990) 31-37.
Schmued, L., “Fluoro-Gold and 4-Acetamido-4′-isothiocyanostilbene-2,2’disulfonic Acid: Use of Substituted Stilbenes in Neuroanatomical Studies,” Methods in Neurosciences, 3 (1990) 317-330.
Schmued, L., Kyriakidis, K., & Heimer, L., In vivo anterograde and retrograde axonal transport of the fluorescent rhodamine-dextran-amine, Fluoro-Ruby, within the CNS. Brain Res, 526 (1990) 127-134.
Schmued, L.C., Kyriakidis, K., Fallon, J.H., and Ribak, C.E., “Neurons containing retrogradely transported Fluoro-Gold exhibit a variety of iysosomal profiles: a combined brightfield, fluorescence and electron microscopic study,” Journal of Neurocytology, 18 (1989) 333-343.
*Pieribone, V.A., Aston-Jones, G., “The iontophoretic application of Flouro-Gold for the study of the afferents to deep brain nuclei,” Brain Research 475 (1988) 259-271. [Link]
Reep, R.L., Baccala, M.J., Booth, M.P., and Goodwin, G.S., “Combined retrograde and anterograde tracing of neuronal connections: Fluoro-Gold and autoradiography,” Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 23 (1988) 1-5.
*Schmued, L.C. and Fallon, J.H., “Fluoro-Gold: a fluorescent retrograde axonal tracer with numerous unique properties,” Brain Research, 377 (1986) 147-154.